Frequently Asked Questions
Some queries and doubts
-
What is Section 80G?
Contributions made to certain relief funds and charitable institutions can be claimed as a deduction under Section 80G of the Income Tax Act. All donations, however, are not eligible for deductions under Section 80G.
-
Who can claim 80G deduction?
- Donations should be made to approved recipients.
- In addition to the receipt for such donations, a certificate is required to take advantage of the deduction.
- A donation made in kind cannot be deducted.
- If a cash donation exceeds Rs. 2,000, it cannot be deducted. (i.e. The donation should be made in any mode of payment other than cash if it exceeds Rs. 2,000)
-
What is amount of tax deduction available
under Section 80G?
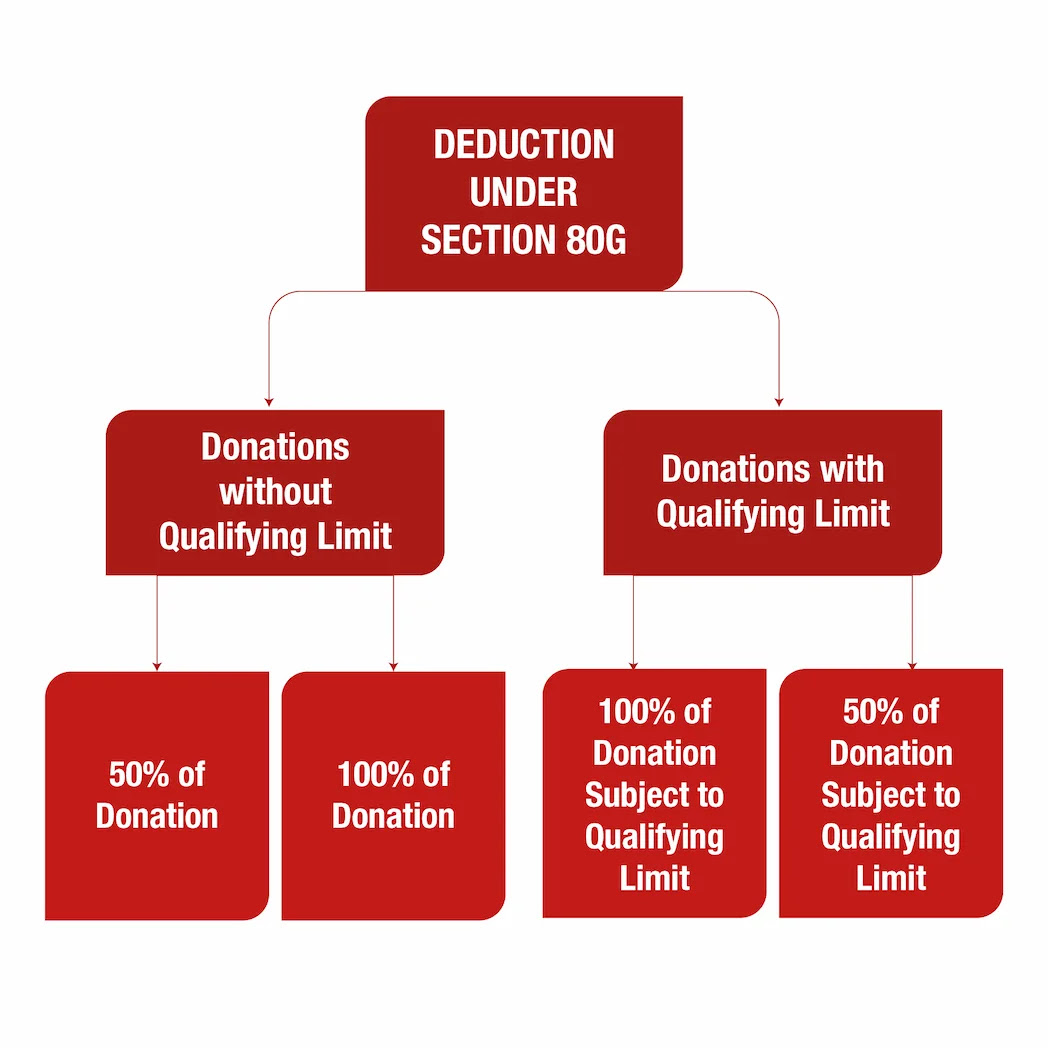
Amount of Deduction is based on the Donee to whom the Donation is made. The following amount of Deduction is available based on categories of donation:
- 100% of Category 1 donation
- 50% of Category 2 donation
- 100% of Category 3 - Subject to the qualifying limit (maximum limit is called qualifying limit)
- 50% of Category 4 - Subject to the qualifying limit (maximum limit is called qualifying limit)
What is the Qualifying Limit?
All donations made to donees (recipients) listed in Category 3 and 4 combined should not exceed 10% of Adjusted Gross Total Income.
-
What are the categories of donations?
Donations fall into the following categories:
Category 1 - Donations eligible for 100% deduction without qualifying limit
- National Defence Fund set up by the Central Government
- Prime Minister’s National Relief Fund
- National Foundation for Communal Harmony
- An approved university/educational institution of National eminence
- Zila Saksharta Samiti constituted in any district under the chairmanship of the Collector of that district
- Fund set up by a state government for the medical relief to the poor
- National Illness Assistance Fund
- National Blood Transfusion Council or to any State Blood Transfusion Council
- National Trust for Welfare of Persons with Autism, Cerebral Palsy, Mental Retardation, and Multiple Disabilities
- National Sports Fund
- National Cultural Fund
- Fund for Technology Development and Application
- National Children’s Fund
- Chief Minister’s Relief Fund or Lieutenant Governor’s Relief Fund with respect to any State or Union Territory
- The Army Central Welfare Fund or the Indian Naval Benevolent Fund or the Air Force Central Welfare Fund, Andhra Pradesh Chief Minister’s Cyclone Relief Fund, 1996
- The Maharashtra Chief Minister’s Relief Fund during October 1, 1993, and October 6, 1993
- Chief Minister’s Earthquake Relief Fund, Maharashtra
- Any fund set up by the State Government of Gujarat exclusively for providing relief to the victims of the earthquake in Gujarat
- Any trust, institution or fund to which Section 80G(5C) applies for providing relief to the victims of the earthquake in Gujarat (contribution made during January 26, 2001, and September 30, 2001)
- Prime Minister’s Armenia Earthquake Relief Fund
- Africa (Public Contributions – India) Fund
- Swachh Bharat Kosh (applicable from FY 2014-15)
- Clean Ganga Fund (applicable from FY 2014-15)
- National Fund for Control of Drug Abuse (applicable from FY 2015-16)
Category 2 - Donations eligible for 50% deduction without qualifying limit
- The Jawaharlal Nehru Memorial Fund,
- Prime Minister’s Drought Relief Fund,
- Indira Gandhi Memorial Trust,
- Rajiv Gandhi Foundation
Category 3 - Donations eligible for 100% deduction subject to qualifying limit
- Donation to Government or any approved local authority for the promotion of Family Planning.
Category 4 - Donations eligible for 50% deduction subject to qualifying limit
- Donations to Charitable institutions who provide a certificate.
-
What changes are made under Budget 2020?
The following modifications to Section 80G will take effect from FY 2020-21:
- Currently, the taxpayer (donor) must manually enter the complete data of the donee (the person to whom the donation is made). However, it was proposed that the donee's information be prefilled in the Income Tax Returns to make the process easier.
- The donee must provide a statement of all donations received on the assumption that the doner would be eligible for a deduction under Section 80G. If the donee fails to provide such a statement, a penalty and fee will be imposed.
- In accordance with the new tax rates announced in the Budget for FY 2020-21 (AY 2021-22), the taxpayer can claim the reduced tax rate if they choose not to take advantage of various deductions and exemptions, except Section 80CCD(2) and Section 80JJAA. If you want to claim tax benefits under Sections 80C, 80D, 80G, HRA, etc., then you should opt for old tax rates.
-
How to calculate the deductible amount
under Section 80G?
The following are the steps to calculate the deduction under Section 80G:
- Determine which category the fund/charitable organisation belongs to (100 percent or 50% deduction with or without a maximum / qualifying limit). For your convenience, we have the entire list is mentioned earlier is this blog.
- If the payment is made to the first category, no additional calculations are required; simply claim 100% or 50% of the donation amount as taxable income.
- Before making a payment to the second category, you must first determine the maximum/qualifying limit. 10% of "adjusted gross total income" is the highest / qualifying limit.
Further, to calculate the amount of deduction, use this formula:
- Gross Qualifying Limit = All donations made to Category - 2
- Net Qualifying Limit = It is 10% of the “adjusted gross total income”.
- Amount Deductible = 100% or 50% of the donation amount subject to the qualifying limit.
-
What is “adjusted gross total income”?
For calculation of tax exemption under Section 80G, the "adjusted gross total income" refers to the total amount of your earnings under all headings less (minus) the following amounts:
- Deductible amount under Sections 80C and 80U of the Income Tax Act (Except 80G)
- Income from which no tax is due (payable)
- Under Section 112 and Section 112A, long-term capital gains that have been included in gross total income.
- Under Section 111A the short-term capital gains
- Income described in Sections 115A, 115AB, 115AC, or 115AD of the Income Tax Act.
Further, to calculate the amount of deduction, use this formula:
- Gross Qualifying Limit = All donations made to Category - 2
- Net Qualifying Limit = It is 10% of the “adjusted gross total income”.
- Amount Deductible = 100% or 50% of the donation amount subject to the qualifying limit.
-
What is the difference between Section
80G Section 80GGB, and Section 80GGC?
Section 80G, Section 80GGB, and Section 80GGC have significant differences. People frequently confuse Section 80G with Section 80GGC or Section 80GGB while filing tax returns.
Since all three sections deal with claiming tax deductions for charitable contributions made in the previous financial year, they differ in the following ways:
- Donations to charitable organizations and trusts are tax deductible under Section 80G.
- Section 80GGB allows registered Indian firms to claim tax deductions for donations to political parties.
- Other taxpayers, such as individuals, HUFs, and corporations, can claim tax deductions for donations given to political parties under Section 80GGC.
-
What is 80 G & 12 A Registration
You donate because you are compelled to do so by an innate desire. After all, giving is more pleasurable than receiving. Most of us believe that selfless giving is a religious belief held by many communities. However, the ability to claim tax deductions on gifts will be a bonus for donors. And this is achievable if your NGOs are registered under 12A and 80G.
Donors will be able to take advantage of tax benefits by obtaining 12A registration for your NGO (Non-Governmental Organization). It is the first step that NGOs must do before providing services to non-profit organizations such as Charitable Trusts and NPOs (Non-Profit Organizations).This provision of tax exemption benefits not only the organization, but also the donors who are linked with it. Previously, registration under 12A was a one-time process; once accepted, the registration remained valid until it was cancelled. However, beginning April 1, 2021, the registration will be granted for a term of five years only, and the organization will be required to apply for renewal every five years. -
What exactly is an 80G Certificate?
The Income Tax Department issues 80G certificates to non-profit organizations under the Income Tax Act of 1961.The major goal of the 80G Registration grant is to encourage more people to donate money to organizations.Furthermore, the donors are excused from paying 50% of their total taxable income in taxes. The donor must attach the stamped receipt to the donation issued by the NGO to qualify for this exemption.
-
What is 12A Registration, and how does it
work?
12A Registration is the first step for non-profits seeking a Certificate of Exemption from the Internal Revenue Service.Companies that are registered under Section 12A are not required to pay income tax since they are exempt.Furthermore, because 12A Registration serves as a genuine documentation of your NGO's existence, it aids you in obtaining approval from the government and organizations abroad.
-
What is Importance of Registrations 12A
and 80G
All NGOs, whether they are a Trust, Society, or Section 8 Company, should register under the 12A and 80G Acts.
The Income Tax Department will grant a total exemption to a non-profit organization having a 12A registration. Those with 80G Certification, on the other hand, have the advantage of attracting more donors to the organization for monetary donations.You will be liable to standard tax rates if you do not secure such Registrations as an NGO. Moreover, recruiting donors for gifts has grown difficult.
 Sanskar Trust
Sanskar Trust